Comprehensive review (behind paywall) Tales of Human Migration, Admixture, and Selection in Africa, by Carina M. Schlebusch & Mattias Jakobsson, Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics (2018), Vol. 9.
Abstract (emphasis mine):
In the last three decades, genetic studies have played an increasingly important role in exploring human history. They have helped to conclusively establish that anatomically modern humans first appeared in Africa roughly 250,000–350,000 years before present and subsequently migrated to other parts of the world. The history of humans in Africa is complex and includes demographic events that influenced patterns of genetic variation across the continent. Through genetic studies, it has become evident that deep African population history is captured by relationships among African hunter–gatherers, as the world’s deepest population divergences occur among these groups, and that the deepest population divergence dates to 300,000 years before present. However, the spread of pastoralism and agriculture in the last few thousand years has shaped the geographic distribution of present-day Africans and their genetic diversity. With today’s sequencing technologies, we can obtain full genome sequences from diverse sets of extant and prehistoric Africans. The coming years will contribute exciting new insights toward deciphering human evolutionary history in Africa.
Regarding potential Afroasiatic origins and expansions:
It is currently believed that farming practices in northeastern and eastern Africa developed independently in the Sahara/Sahel (around 7,000 BP) and the Ethiopian highlands (7,000–4,000 BP), while farming in the Nile River Valley developed as a consequence of the Neolithic Revolution in the Middle East (84). Northeastern and eastern African farmers today speak languages from the Afro-Asiatic and Nilo-Saharan linguistic groups, which is also reflected in their genetic affinities (Figure 3, K=6). In the northern parts of East Africa (South Sudan, Somalia, and Ethiopia), Nilo-Saharan and Afro-Asiatic speakers with farming lifeways have completely replaced hunter–gatherers. It is still largely unclear how farming and herding practices influenced the northeastern African prefarming population structure and whether the spread of farming is better explained by demic or cultural diffusion in this part of the world. Genetic studies of contemporary populations and aDNA have started to provide some insights into population continuity and incoming gene flow in this region of Africa.
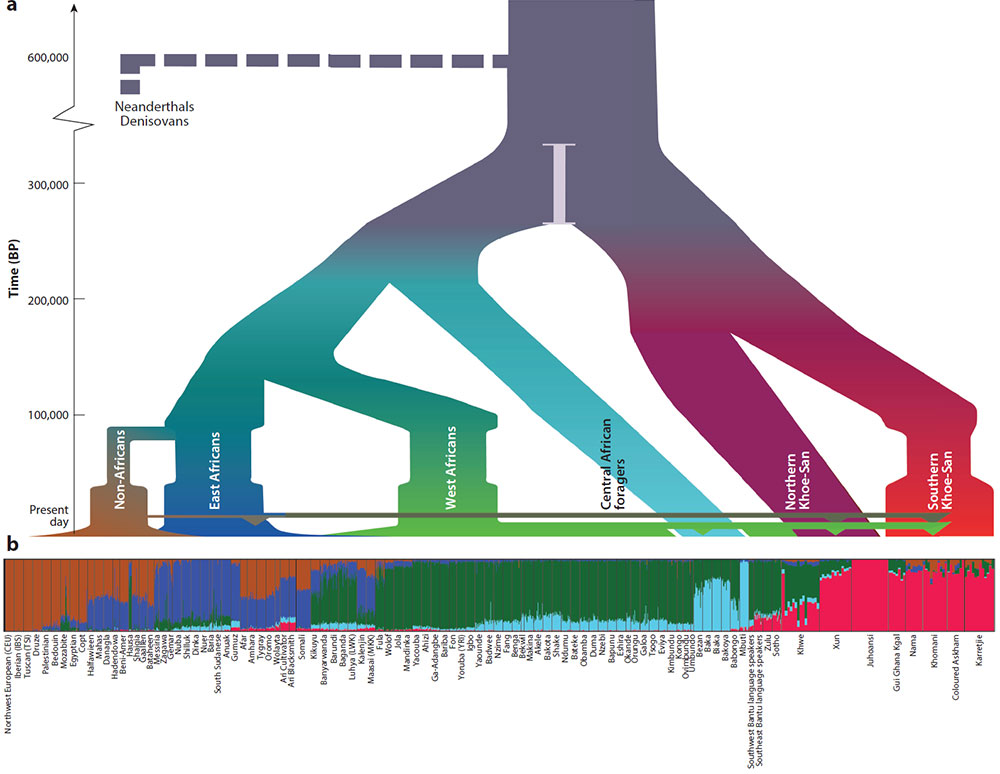
For example, studies have shown that a back-migration from Eurasia into Africa affected most of northeastern and eastern Africa (36, 46, 53, 89, 132) (Figure 1b). A genetic baseline of eastern African ancestral genetic variation unaffected by recent Eurasian admixture and farming migrations within the last 4,500 years has been suggested in the form of the genome sequence of a 4,500-year-old individual from Mota, Ethiopia (36). Based on comparisons with the ancient Mota genome, we know that certain populations from northeastern Africa show deep continuity in their local area with very limited gene flow resulting from recent population movements. For example, the Nilotic herder populations from South Sudan (e.g., Dinka, Nuer, and Shilluk) appear to have remained relatively isolated over time and received little to no gene flow from Eurasians, West African Bantu-speaking farmers, and other surrounding groups (53) (Figures 2 and 3). By contrast, the Nubian and Arab populations to their north show gene flow with Eurasians, which has been connected to the Arab expansion (53). The Nubian, Arab, and Beja populations of northeastern Africa roughly display equal admixture fractions from a local northeastern African gene pool (similar to the Nilotic component) and an incoming Eurasian migrant component (53) (Figure 3). The Eurasian component has been linked to the Middle East and the Arab migration, but only the Arab groups shifted to the Semitic languages; the Nubians and Beja groups kept their original languages. The Eurasian gene flow appears to have spread from north to south along the Nile and Blue Nile in a succession of admixture events (53).
Skoglund and Mathieson’s preprint has also been published in the same volume, without meaningful changes.
Related:
- Pleistocene North African genomes link Near Eastern and sub-Saharan African human populations
- Genetic ancestry of Hadza and Sandawe peoples reveals ancient population structure in Africa
- R1b-V88 migration through Southern Italy into Green Sahara corridor, and the Afroasiatic connection
- Potential Afroasiatic Urheimat near Lake Megachad
- Expansion of peoples associated with spread of haplogroups: Mongols and C3*-F3918, Arabs and E-M183 (M81)
- Genetic landscapes showing human genetic diversity aligning with geography
- Human ancestry solves language questions? New admixture citebait